Demographics of Namibia
| Demographics of Namibia | |
|---|---|
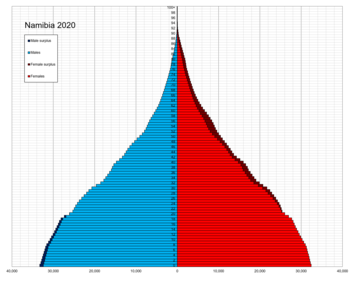 Population pyramid of Namibia in 2020 | |
| Population | 2,727,409 (2022 est.) |
| Growth rate | 1.82% (2022 est.) |
| Birth rate | 25.01 births/1,000 population (2022 est.) |
| Death rate | 6.85 deaths/1,000 population (2022 est.) |
| Life expectancy | 66.47 years |
| • male | 64.46 years |
| • female | 68.53 years |
| Fertility rate | 2.98 children born/woman (2022 est.) |
| Infant mortality rate | 29.42 deaths/1,000 live births |
| Net migration rate | 0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2022 est.) |
| Age structure | |
| 0–14 years | 35.68% |
| 65 and over | 3.9% |
| Nationality | |
| Nationality | Namibian |
This is a demography of the population of Namibia including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
Population
[edit]

Census results
[edit]| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1921 | 228,916 | — |
| 1936 | 320,457 | +2.27% |
| 1946 | 362,464 | +1.24% |
| 1951 | 439,081 | +3.91% |
| 1970 | 761,010 | +2.94% |
| 1981 | 1,033,196 | +2.82% |
| 1991 | 1,409,915 | +3.16% |
| 2001 | 1,830,330 | +2.64% |
| 2011 | 2,113,077 | +1.45% |
| 2023 | 3,022,401 | +3.03% |
As required by the Namibian Statistics Act #66 of 1976, and in accordance with United Nations recommendations, a census is conducted every ten years. After Namibian independence the first Population and Housing Census was carried out in 1991, further rounds followed in 2001 and 2011.[1] The data collection method is to count every person resident in Namibia wherever they happen to be. This is called the de facto method.[2] For enumeration purposes the country is demarcated into 4,042 enumeration areas. These areas overlap with constituency boundaries in order to get reliable data for election purposes as well.[3]
The 2011 Population and Housing Census counted 2,113,077 inhabitants of Namibia. Between 2001 and 2011 the annual population growth was 1.4%, down from 2.6% in the previous ten–year period.[4]
In 2011 the total fertility rate was 3.6 children per woman, down from 4.1 in 2001.
UN estimates
[edit]According to the 2022 revision of the World Population Prospects[5][6] the total population was 2,530,151 in 2021, compared to only 485 000 in 1950. The proportion of children below the age of 15 in 2010 was 36.4%, 59.9% was between 15 and 65 years of age, while 3.7% was 65 years or older .[7]
| Total population | Population aged 0–14 (%) | Population aged 15–64 (%) | Population aged 65+ (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 485 000 | 38.8 | 57.1 | 4.1 |
| 1955 | 538 000 | 40.5 | 55.6 | 4.0 |
| 1960 | 603 000 | 41.6 | 54.7 | 3.7 |
| 1965 | 683 000 | 42.5 | 53.9 | 3.6 |
| 1970 | 780 000 | 43.1 | 53.3 | 3.6 |
| 1975 | 906 000 | 44.3 | 52.2 | 3.5 |
| 1980 | 1 013 000 | 46.6 | 49.9 | 3.5 |
| 1985 | 1 150 000 | 47.0 | 49.5 | 3.5 |
| 1990 | 1 415 000 | 43.7 | 53 | 3.4 |
| 1995 | 1 651 000 | 42 | 54.6 | 3.4 |
| 2000 | 1 896 000 | 40.3 | 56.3 | 3.4 |
| 2005 | 2 080 000 | 38.9 | 57.6 | 3.4 |
| 2010 | 2 283 000 | 36.4 | 59.9 | 3.7 |
Population Estimates by Sex and Age Group (01.VII.2020) (Based on the results of the 2011 Population Census.):[8]
| Age Group | Male | Female | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 1 217 976 | 1 286 522 | 2 504 498 | 100 |
| 0–4 | 168 415 | 164 699 | 333 114 | 13.30 |
| 5–9 | 157 646 | 154 774 | 312 420 | 12.47 |
| 10–14 | 137 092 | 135 235 | 272 327 | 10.87 |
| 15–19 | 118 166 | 117 873 | 236 039 | 9.42 |
| 20–24 | 118 207 | 121 535 | 239 742 | 9.57 |
| 25–29 | 110 095 | 115 411 | 225 506 | 9.00 |
| 30–34 | 94 967 | 99 744 | 194 711 | 7.77 |
| 35–39 | 74 591 | 80 644 | 155 235 | 6.20 |
| 40–44 | 61 719 | 67 206 | 128 925 | 5.15 |
| 45–49 | 49 370 | 56 034 | 105 404 | 4.21 |
| 50–54 | 37 319 | 44 620 | 81 939 | 3.27 |
| 55–59 | 28 792 | 37 243 | 66 035 | 2.64 |
| 60–64 | 20 002 | 28 448 | 48 450 | 1.93 |
| 65–69 | 15 303 | 21 162 | 36 465 | 1.46 |
| 70–74 | 11 841 | 16 460 | 28 301 | 1.13 |
| 75–79 | 6 904 | 11 064 | 17 968 | 0.72 |
| 80+ | 7 547 | 14 370 | 21 917 | 0.88 |
| Age group | Male | Female | Total | Percent |
| 0–14 | 463 153 | 454 708 | 917 861 | 36.65 |
| 15–64 | 713 228 | 768 758 | 1 481 986 | 59.17 |
| 65+ | 41 595 | 63 056 | 104 651 | 4.18 |
Vital statistics
[edit]Registration of vital events in Namibia is not complete. The website Our World in Data prepared the following estimates based on statistics from the Population Department of the United Nations.[9]
| Mid-year population | Live births | Deaths | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1000) | Crude death rate (per 1000) | Natural change (per 1000) | Total fertility rate (TFR) | Infant mortality (per 1000 live births) | Life expectancy (in years) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 515 000 | 22 000 | 12 000 | 10 000 | 42.0 | 22.5 | 19.5 | 5.75 | 141.7 | 41.5 |
| 1951 | 521 000 | 22 000 | 12 000 | 10 000 | 42.0 | 22.4 | 19.6 | 5.79 | 140.3 | 41.8 |
| 1952 | 527 000 | 22 000 | 12 000 | 11 000 | 42.0 | 22.0 | 20.0 | 5.83 | 137.6 | 42.4 |
| 1953 | 534 000 | 22 000 | 12 000 | 11 000 | 42.0 | 21.6 | 20.4 | 5.89 | 134.7 | 43.0 |
| 1954 | 540 000 | 23 000 | 11 000 | 11 000 | 41.9 | 21.1 | 20.8 | 5.93 | 131.8 | 43.7 |
| 1955 | 547 000 | 23 000 | 11 000 | 12 000 | 41.7 | 20.7 | 21.1 | 5.97 | 128.8 | 44.3 |
| 1956 | 555 000 | 23 000 | 11 000 | 12 000 | 41.6 | 20.2 | 21.4 | 6.01 | 125.7 | 44.9 |
| 1957 | 562 000 | 23 000 | 11 000 | 12 000 | 41.6 | 19.7 | 21.8 | 6.05 | 122.6 | 45.6 |
| 1958 | 571 000 | 24 000 | 11 000 | 13 000 | 41.6 | 19.2 | 22.3 | 6.10 | 119.4 | 46.3 |
| 1959 | 580 000 | 24 000 | 11 000 | 13 000 | 41.6 | 18.8 | 22.8 | 6.14 | 116.1 | 46.9 |
| 1960 | 590 000 | 25 000 | 11 000 | 14 000 | 41.8 | 18.2 | 23.5 | 6.21 | 112.9 | 47.7 |
| 1961 | 601 000 | 25 000 | 11 000 | 15 000 | 42.0 | 17.8 | 24.2 | 6.27 | 109.7 | 48.4 |
| 1962 | 614 000 | 26 000 | 11 000 | 15 000 | 42.3 | 17.3 | 25.0 | 6.34 | 106.6 | 49.1 |
| 1963 | 627 000 | 27 000 | 11 000 | 16 000 | 42.6 | 16.9 | 25.7 | 6.40 | 103.5 | 49.7 |
| 1964 | 642 000 | 28 000 | 11 000 | 17 000 | 42.8 | 16.4 | 26.3 | 6.43 | 100.6 | 50.4 |
| 1965 | 658 000 | 28 000 | 11 000 | 18 000 | 43.0 | 16.0 | 26.9 | 6.46 | 97.8 | 51.0 |
| 1966 | 675 000 | 29 000 | 11 000 | 18 000 | 43.1 | 15.7 | 27.4 | 6.49 | 95.1 | 51.4 |
| 1967 | 693 000 | 30 000 | 11 000 | 19 000 | 43.3 | 15.4 | 27.9 | 6.51 | 92.5 | 52.0 |
| 1968 | 712 000 | 31 000 | 11 000 | 20 000 | 43.5 | 15.0 | 28.5 | 6.54 | 90.1 | 52.6 |
| 1969 | 733 000 | 32 000 | 11 000 | 21 000 | 43.6 | 14.6 | 29.0 | 6.55 | 87.7 | 53.1 |
| 1970 | 754 000 | 33 000 | 11 000 | 22 000 | 43.7 | 14.3 | 29.4 | 6.55 | 85.4 | 53.6 |
| 1971 | 777 000 | 34 000 | 11 000 | 23 000 | 43.9 | 13.9 | 30.0 | 6.55 | 83.1 | 54.2 |
| 1972 | 801 000 | 35 000 | 11 000 | 24 000 | 43.9 | 13.5 | 30.4 | 6.55 | 80.8 | 54.8 |
| 1973 | 825 000 | 36 000 | 11 000 | 26 000 | 44.1 | 13.1 | 30.9 | 6.56 | 78.6 | 55.4 |
| 1974 | 850 000 | 37 000 | 11 000 | 27 000 | 44.1 | 12.8 | 31.3 | 6.56 | 76.3 | 55.9 |
| 1975 | 877 000 | 39 000 | 11 000 | 28 000 | 43.9 | 12.4 | 31.5 | 6.54 | 74.2 | 56.5 |
| 1976 | 902 000 | 39 000 | 11 000 | 28 000 | 43.5 | 12.0 | 31.5 | 6.50 | 72.2 | 57.0 |
| 1977 | 926 000 | 40 000 | 11 000 | 29 000 | 42.9 | 11.7 | 31.3 | 6.45 | 70.5 | 57.6 |
| 1978 | 942 000 | 40 000 | 11 000 | 30 000 | 42.3 | 11.3 | 31.0 | 6.38 | 69.0 | 58.1 |
| 1979 | 957 000 | 39 000 | 11 000 | 29 000 | 41.0 | 11.1 | 29.9 | 6.32 | 67.6 | 58.4 |
| 1980 | 976 000 | 40 000 | 11 000 | 28 000 | 40.6 | 11.6 | 28.9 | 6.25 | 66.3 | 56.8 |
| 1981 | 987 000 | 40 000 | 11 000 | 28 000 | 39.7 | 11.4 | 28.4 | 6.16 | 64.9 | 57.1 |
| 1982 | 1 006 000 | 39 000 | 11 000 | 28 000 | 38.6 | 11.0 | 27.6 | 6.08 | 63.3 | 57.6 |
| 1983 | 1 033 000 | 40 000 | 11 000 | 29 000 | 38.5 | 10.8 | 27.8 | 6.00 | 61.5 | 58.0 |
| 1984 | 1 062 000 | 41 000 | 11 000 | 30 000 | 38.5 | 10.4 | 28.1 | 5.93 | 59.5 | 58.5 |
| 1985 | 1 093 000 | 42 000 | 11 000 | 31 000 | 38.5 | 10.1 | 28.3 | 5.85 | 57.3 | 59.0 |
| 1986 | 1 128 000 | 43 000 | 11 000 | 32 000 | 38.5 | 9.8 | 28.7 | 5.77 | 55.0 | 59.6 |
| 1987 | 1 165 000 | 45 000 | 11 000 | 34 000 | 38.7 | 9.5 | 29.2 | 5.67 | 52.8 | 60.2 |
| 1988 | 1 208 000 | 47 000 | 11 000 | 36 000 | 38.9 | 9.4 | 29.5 | 5.58 | 51.0 | 60.2 |
| 1989 | 1 288 000 | 49 000 | 10 000 | 39 000 | 39.3 | 8.4 | 30.9 | 5.47 | 49.2 | 62.6 |
| 1990 | 1 369 000 | 55 000 | 11 000 | 44 000 | 40.6 | 8.3 | 32.2 | 5.32 | 48.0 | 62.5 |
| 1991 | 1 416 000 | 57 000 | 12 000 | 45 000 | 40.1 | 8.4 | 31.6 | 5.23 | 47.0 | 62.1 |
| 1992 | 1 462 000 | 57 000 | 13 000 | 45 000 | 39.1 | 8.6 | 30.5 | 5.07 | 46.4 | 61.5 |
| 1993 | 1 510 000 | 57 000 | 13 000 | 44 000 | 37.8 | 8.8 | 29.1 | 4.89 | 46.1 | 60.9 |
| 1994 | 1 558 000 | 57 000 | 14 000 | 42 000 | 36.3 | 9.1 | 27.2 | 4.67 | 46.4 | 59.8 |
| 1995 | 1 605 000 | 55 000 | 15 000 | 40 000 | 34.6 | 9.5 | 25.1 | 4.43 | 47.2 | 58.6 |
| 1996 | 1 650 000 | 54 000 | 17 000 | 38 000 | 33.1 | 10.2 | 22.8 | 4.21 | 48.1 | 56.9 |
| 1997 | 1 693 000 | 55 000 | 18 000 | 37 000 | 32.6 | 10.8 | 21.8 | 4.15 | 48.9 | 55.6 |
| 1998 | 1 736 000 | 56 000 | 20 000 | 36 000 | 32.6 | 11.6 | 21.0 | 4.15 | 49.5 | 54.1 |
| 1999 | 1 778 000 | 57 000 | 22 000 | 36 000 | 32.3 | 12.1 | 20.1 | 4.11 | 49.8 | 53.0 |
| 2000 | 1 819 000 | 57 000 | 23 000 | 34 000 | 31.4 | 12.7 | 18.7 | 3.98 | 49.8 | 52.0 |
| 2001 | 1 856 000 | 56 000 | 24 000 | 32 000 | 30.4 | 13.1 | 17.3 | 3.83 | 49.7 | 51.3 |
| 2002 | 1 889 000 | 56 000 | 25 000 | 31 000 | 29.7 | 13.1 | 16.6 | 3.72 | 49.1 | 51.3 |
| 2003 | 1 915 000 | 56 000 | 25 000 | 31 000 | 29.2 | 13.2 | 15.9 | 3.62 | 49.0 | 51.1 |
| 2004 | 1 939 000 | 56 000 | 26 000 | 31 000 | 29.0 | 13.2 | 15.8 | 3.58 | 48.9 | 51.2 |
| 2005 | 1 963 000 | 57 000 | 25 000 | 32 000 | 29.0 | 13.0 | 16.1 | 3.56 | 46.8 | 51.8 |
| 2006 | 1 987 000 | 58 000 | 25 000 | 33 000 | 29.0 | 12.5 | 16.5 | 3.54 | 43.9 | 52.7 |
| 2007 | 2 011 000 | 59 000 | 24 000 | 35 000 | 29.3 | 12.0 | 17.2 | 3.55 | 41.2 | 53.7 |
| 2008 | 2 039 000 | 61 000 | 24 000 | 37 000 | 29.7 | 11.6 | 18.1 | 3.59 | 38.1 | 54.7 |
| 2009 | 2 068 000 | 62 000 | 23 000 | 39 000 | 30.1 | 11.2 | 18.9 | 3.61 | 36.2 | 55.5 |
| 2010 | 2 099 000 | 64 000 | 23 000 | 41 000 | 30.4 | 11.1 | 19.4 | 3.63 | 34.3 | 56.0 |
| 2011 | 2 132 000 | 66 000 | 23 000 | 43 000 | 30.8 | 10.9 | 19.9 | 3.66 | 34.6 | 56.6 |
| 2012 | 2 167 000 | 67 000 | 23 000 | 45 000 | 31.1 | 10.4 | 20.7 | 3.68 | 35.0 | 57.6 |
| 2013 | 2 205 000 | 68 000 | 22 000 | 46 000 | 30.9 | 9.9 | 21.0 | 3.65 | 34.2 | 58.7 |
| 2014 | 2 243 000 | 69 000 | 21 000 | 48 000 | 30.7 | 9.4 | 21.3 | 3.64 | 33.5 | 59.8 |
| 2015 | 2 283 000 | 70 000 | 21 000 | 49 000 | 30.4 | 9.1 | 21.3 | 3.60 | 33.4 | 60.7 |
| 2016 | 2 323 000 | 70 000 | 20 000 | 50 000 | 30.1 | 8.7 | 21.4 | 3.57 | 32.5 | 61.7 |
| 2017 | 2 365 000 | 70 000 | 20 000 | 50 000 | 29.5 | 8.5 | 21.0 | 3.51 | 31.6 | 62.3 |
| 2018 | 2 406 000 | 70 000 | 20 000 | 50 000 | 29.0 | 8.4 | 20.6 | 3.46 | 31.0 | 62.6 |
| 2019 | 2 447 000 | 70 000 | 20 000 | 49 000 | 28.4 | 8.2 | 20.2 | 3.40 | 29.8 | 63.1 |
| 2020 | 2 688 000 | 76 000 | 21 000 | 55 000 | 27.7 | 7.5 | 20.2 | 3.35 | 29.5 | 64.1 |
| 2021 | 2 770 000 | 76 000 | 26 000 | 50 000 | 27.0 | 9.2 | 17.8 | 3.30 | 28.7 | 60.9 |
| 2022 | 2 851 000 | 76 000 | 22 000 | 55 000 | 27.9 | 7.5 | 18.9 | 3.25 | 28.7 | 64.2 |
| 2023 | 2 928 000 | 77 000 | 18 000 | 58 000 | 25.9 | 6.2 | 19.7 | 3.21 | 27.2 | 67.4 |
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. Updates on reimplementing the Graph extension, which will be known as the Chart extension, can be found on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. Updates on reimplementing the Graph extension, which will be known as the Chart extension, can be found on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. Updates on reimplementing the Graph extension, which will be known as the Chart extension, can be found on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. Updates on reimplementing the Graph extension, which will be known as the Chart extension, can be found on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Fertility and births
[edit]Total Fertility Rate (TFR) (followed by wanted fertility rate in brackets) and Crude Birth Rate (CBR):[10]
| Year | Total | Urban | Rural | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBR | TFR | CBR | TFR | CBR | TFR | |
| 1992 | 42 | 5.4 (4.8) | 43 | 4.0 (3.4) | 42 | 6.3 (5.8) |
| 2000 | 30.5 | 4.2 (3.4) | 29.9 | 3.1 (2.4) | 30.8 | 5.1 (4.2) |
| 2006–2007 | 29.2 | 3.6 (2.7) | 28.8 | 2.8 (2.2) | 29.6 | 4.3 (3.3) |
| 2013 | 29.5 | 3.6 (2.9) | 30.0 | 2.9 (2.4) | 29.3 | 4.7 (3.5) |
Fertility data as of 2013 (DHS Program):[11]
| Region | Total fertility rate | Percentage of women age 15–49 currently pregnant | Mean number of children ever born to women age 40–49 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zambezi | 4.2 | 4.5 | 4.4 |
| Erongo | 2.9 | 6.1 | 3.3 |
| Hardap | 3.7 | 3.8 | 3.4 |
| Karas | 3.4 | 6.4 | 3.4 |
| Kavango | 4.6 | 6.8 | 5.4 |
| Khomas | 2.6 | 6.4 | 2.7 |
| Kunene | 4.5 | 8.5 | 4.6 |
| Ohangwena | 5.3 | 9.8 | 5.2 |
| Omaheke | 4.6 | 8.6 | 4.2 |
| Omusati | 4.2 | 6.3 | 3.6 |
| Oshana | 2.7 | 6.2 | 3.1 |
| Oshikoto | 4.2 | 5.7 | 4.0 |
| Otjozondjupa | 4.1 | 5.4 | 4.0 |
Life expectancy at birth
[edit]Life expectancy from 1950 to 2015 (UN World Population Prospects):[12]
| Period | Life expectancy in Years |
|---|---|
| 1950–1955 | 41.75 |
| 1955–1960 | |
| 1960–1965 | |
| 1965–1970 | |
| 1970–1975 | |
| 1975–1980 | |
| 1980–1985 | |
| 1985–1990 | |
| 1990–1995 | |
| 1995–2000 | |
| 2000–2005 | |
| 2005–2010 | |
| 2010–2015 |
Ethnic groups
[edit]Namibia has many ethnic groups. The 9 main ethnic groups are:
The majority of the Namibian population is of Bantu-speaking origin—mostly of the Ovambo ethnicity, which forms about half of the population—residing mainly in the north of the country, although many are now resident in towns throughout Namibia. They also include the Lozi people and Kavango people. Other ethnic groups are the Herero and Himba people, who speak a similar language, and the Damara, who speak the same "click" language as the Nama. As of 2022[update] Herero and Nama peoples make up less than 10% of the population, but at the beginning of the 20th century and before the Herero and Namaqua Genocide, they made up a majority.[13]
In addition to the Bantu majority, there are large groups of San, who are descendants of the original culture of Southern Africa, as well as Nama who are descendants of the above as well as mixed with colonists. They often speak Khoekhoegowab. The country also contains some descendants of refugees from Angola. There are also two smaller groups of people with mixed racial origins, called "Coloureds" and "Basters", who together make up 8.0% (with the Coloureds outnumbering the Basters two to one). There is a substantial Chinese minority in Namibia; it stood at 40,000 in 2006.[14]

Whites (mainly of Afrikaner, German, British and Portuguese origin) make up between 4.0 and 7.0% of the population. Although their proportion of the population decreased after independence due to emigration and lower birth rates, they still form the second-largest population of European ancestry, both in terms of percentage and actual numbers, in Sub-Saharan Africa (after South Africa/Angola).[15] The majority of Namibian whites and nearly all those who are of mixed race, speak Afrikaans and share similar origins, culture, and religion as the white and coloured populations of South Africa. A large minority of whites (around 30,000) trace their family origins back to the German settlers who colonised Namibia prior to the British confiscation of German lands after World War I, and they maintain German cultural and educational institutions. Nearly all Portuguese settlers came to the country from the former Portuguese colony of Angola.[16] The 1960 census reported 526,004 persons in what was then South West Africa, including 73,464 whites (14%).[17]
Languages
[edit]- Oshiwambo – 48.9%[18]
- Khoekhoegowab – 11.3%
- Afrikaans – 10.4%
- Otjiherero – 8.6%
- RuKwangali – 8.5%
- Silozi – 4.8%
- English (official language) – 3.4%
- Setswana – 0.3%
- Other African languages – 2.3%
- Other – 1.7%







Religion
[edit]Missionary work during the 19th century drew many Namibians to Christianity, especially Lutheranism. While most Namibian Christians are Lutheran, there also are Roman Catholic, Methodist, Anglican, African Methodist Episcopal, and Dutch Reformed Christians represented.
- Christian 80% to 90% (at least 50% Lutheran)[18]
- Indigenous beliefs 10% to 20%
Other demographic statistics
[edit]Modern education and medical care have been extended in varying degrees to most rural areas in recent years. The literacy rate of Africans is generally low except in sections where missionary and government education efforts have been concentrated, such as Ovamboland. The Africans speak various indigenous languages.
Demographic statistics according to the World Population Review in 2022.[19]
- One birth every 8 minutes
- One death every 27 minutes
- One net migrant every 131 minutes
- Net gain of one person every 11 minutes
The following demographic are from the CIA World Factbook[20] unless otherwise indicated.
Population
[edit]- 2,727,409 (2022 est.)
- 2,533,224 (July 2018 est.)
Religions
[edit]Christian 97.5%, other 0.6% (includes Muslim, Baha'i, Jewish, Buddhist), unaffiliated 1.9% (2020 est.)
Age structure
[edit]- 0–14 years: 35.68% (male 473,937/female 464,453)
- 15–24 years: 20.27% (male 267,106/female 265,882)
- 25–54 years: 35.47% (male 449,132/female 483,811)
- 55–64 years: 4.68% (male 54,589/female 68,619)
- 65 years and over: 3.9% (2020 est.) (male 43,596/female 58,948)
- 0–14 years: 36.54% (male 467,392 /female 458,190)
- 15–24 years: 20.34% (male 257,190 /female 257,984)
- 25–54 years: 34.74% (male 421,849 /female 458,118)
- 55–64 years: 4.46% (male 50,459 /female 62,478)
- 65 years and over: 3.93% (male 42,381 /female 57,183) (2018 est.)
Birth rate
[edit]- 25.01 births/1,000 population (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 45th
- 25.33 births/1,000 population (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 45th
Death rate
[edit]- 6.85 deaths/1,000 population (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 124th
- 7.07 deaths/1,000 population (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 117th
- 2.94 children born/woman (2023 est.) Country comparison to the world: 50th
- 2.98 children born/woman (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 48th
- 3.03 children born/woman (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 48th
Median age
[edit]- total: 21.8 years. Country comparison to the world: 183rd
- male: 21.1 years
- female: 22.6 years (2020 est.)
Population growth rate
[edit]- 1.82% (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 50th
- 1.83% (2020 est.) Country comparison to the world: 45th
Mother's mean age at first birth
[edit]- 21.5 years (2013 est.)
- note: median age at first birth among women 25–29[clarification needed]
Contraceptive prevalence rate
[edit]- 56.1% (2013)
Net migration rate
[edit]0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2022 est.) Country comparison to the world: 94th
Urbanization
[edit]- urban population: 54% of total population (2022)
- rate of urbanization: 3.64% annual rate of change (2020–25 est.)
- urban population: 50% of total population (2018)
- rate of urbanization: 4.2% annual rate of change (2015–20 est.)
Major infectious diseases
[edit]- degree of risk: high (2020)
- food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
- vectorborne diseases: malaria
- water contact diseases: schistosomiasis
- total dependency ratio: 68.1 (2015 est.)
- youth dependency ratio: 62.2 (2015 est.)
- elderly dependency ratio: 5.8 (2015 est.)
- potential support ratio: 17.1 (2015 est.)
Education expenditures
[edit]- 9.4% of GDP (2020) Country comparison to the world: 6th
Sex ratio
[edit]at birth:
1.03 male(s)/female (2017 est.)
under 15 years:
1.02 male(s)/female (2017 est.)
15–64 years:
0.99 male(s)/female (2017 est.)
65 years and over:
0.75 male(s)/female (2017 est.)
total population:
0.96 male(s)/female (2017 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
[edit]- total population: 65.87 years (2021 est.) Country comparison to the world: 197th
- male: 63.9 years (2021 est.)
- female: 67.9 years (2021 est.)
HIV/AIDS
[edit]adult prevalence rate: 12.7% (2019 est.) Country comparison to the world: 6th
people living with HIV/AIDS: 210,000 (2019 est.)
deaths: 3,000 (2019 est.)
Nationality
[edit]noun:
Namibian(s)
adjective:
Namibian
Literacy
[edit]definition: age 15 and over can read and write (2015 est.)
- total population: 91.5% (2018 est.)
- male: 91.6% (2018 est.)
- female: 91.4% (2018 est.)
Unemployment, youth ages 15–24
[edit]- total: 38%
- male: 37.5%
- female: 38.5% (2018 est.)
References
[edit]- ^ "Census Summary Results". National Planning Commission of Namibia. Archived from the original on 11 January 2012. Retrieved 21 February 2012.
- ^ Kapitako, Alvine (8 August 2011). "Namibia: 2011 Census Officially Launched". New Era. via allafrica.com.
- ^ "Methodology". National Planning Commission of Namibia. Archived from the original on 11 January 2012. Retrieved 21 February 2012.
- ^ Duddy, Jo Maré (28 March 2013). "Census gives snapshot of Namibia's population". The Namibian.
- ^ "World Population Prospects 2022". United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved July 17, 2022.
- ^ "World Population Prospects 2022: Demographic indicators by region, subregion and country, annually for 1950-2100" (XSLX) ("Total Population, as of 1 July (thousands)"). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved July 17, 2022.
- ^ Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations Secretariat, World Population Prospects: The 2010 Revision Archived May 6, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "UNSD — Demographic and Social Statistics".
- ^ "Population & Demography Data Explorer". Our World in Data. Retrieved 2022-07-22.
- ^ "MEASURE DHS: Demographic and Health Surveys". microdata.worldbank.org.
- ^ "Namibia Demographic and Health Survey 2013" (PDF). Namibia Demographic and Health Survey. 2013.
- ^ "World Population Prospects – Population Division – United Nations". Retrieved 2017-07-15.
- ^ Popp, Maximilian; Riedmann, Bernhard (2022-11-10). "Namibia Continues Seeking Justice for Germany's Colonial-Era Genocide". Der Spiegel. Retrieved 2022-11-10.
- ^ Malia Politzer (August 2008). "China and Africa: Stronger Economic Ties Mean More Migration". Migration Information Source. Retrieved 10 September 2013.
- ^
 This article incorporates public domain material from "Namibia". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). CIA. Retrieved 23 January 2010. (Archived 2009 edition.)
This article incorporates public domain material from "Namibia". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). CIA. Retrieved 23 January 2010. (Archived 2009 edition.)
- ^ "Flight from Angola". The Economist. 16 August 1975. Retrieved 10 September 2013.
- ^ Singh, Lalita Prasad (1980). The United Nations and Namibia. East African Publishing House.
- ^ a b c d
 This article incorporates public domain material from "Namibia". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). CIA. 19 April 2022. (Archived 2022 edition.)
This article incorporates public domain material from "Namibia". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). CIA. 19 April 2022. (Archived 2022 edition.)
- ^ "Namibia Population 2022", World Population Review
- ^
 This article incorporates public domain material from "Namibia". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). CIA. March 4, 2021. (Archived 2021 edition.)
This article incorporates public domain material from "Namibia". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). CIA. March 4, 2021. (Archived 2021 edition.)

